Introduction
Aligning business technology with an organization's strategy and goals can often be a complex and overwhelming process without the right tools and expertise. Enterprise architects are now a valuable part of any modern and traditional enterprise. Enterprise architecture is a strategically and technically high-level role that scales elements of IT architecture for critical use in enterprise environments.
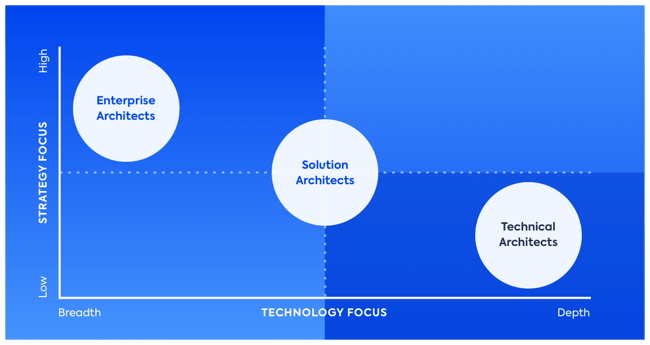
While business transformation employs many skilled and specialist roles, enterprise architects should not be confused with solution, technical, or business architects. While there is an overlap, the overarching purpose of each role differs.
📚 Related: IT Architecture Roles
What is an enterprise architect?
An enterprise architect is an IT professional who ensures an organization’s IT strategy is aligned with its business goals. They analyze business properties, define all business needs, and the external environment.
EAs work closely with stakeholders, management, and SMEs (Subject Matter Experts) to develop and implement an organization's strategy, information, processes, and IT assets. An EA is responsible for using this knowledge to ensure IT and business alignment.
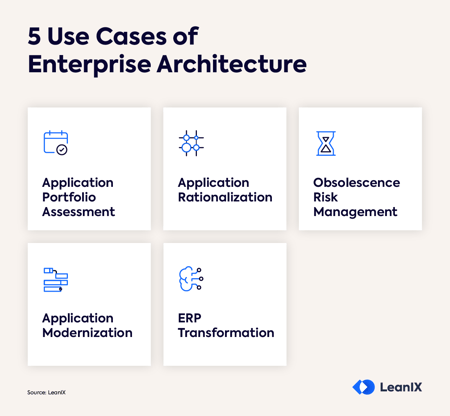
The 5 key use cases of Enterprise Architecture
Role - What does an enterprise architect do?
Among all IT architects, EAs will have the most overarching view of an organization, and vast knowledge of its business capabilities and potential. EAs play a key role in identifying business needs using both external factors (such as competitors) and internal factors (such as the company's IT landscape).
The role of an EA requires strategizing to manage legacy and cloud systems, replace obsolete software, and lead migrations to support business operations across each department.
Depending on the organization, there are several other roles within the enterprise architecture team, such as:
- Chief enterprise architect: The leader of the enterprise architecture team in an organization is referred to as the Chief Enterprise Architect or Chief EA. Usually, this individual is an experienced enterprise architect who also holds leadership responsibilities.
- The Architecture Owner (AO): The AO is responsible for providing guidance to teams, specifically solution delivery teams, in making architecture and solutions decisions. This role may be held by an individual who is also an enterprise architect and works closely with them. The AO is a team-level position and is sometimes referred to as an Agile Solution Architect or Agile Architect.
- Chief architecture owner (CAO): The role of a Chief Architecture Officer (CAO) involves leading the architecture initiatives for a program at a high level. Usually, a CAO is a senior Architecture Owner (AO) with added leadership responsibilities. They collaborate closely with Enterprise Architects (EAs) and may even hold the EA role themselves.
📚 Related: It's a Great Time to be an Enterprise Architect
Day-to-day
While other IT specialists such as technical architects focus on solving day-to-day technology solutions, enterprise architects will be strategizing multi-year roadmaps to enable business growth, ensure compliance and reduce the complexity of key business and IT processes.
During the day-to-day, EAs will play a vital role across the enterprise IT landscape; they will be defining the applications, establishing architecture principles, leading digital transformation, developing enterprise frameworks, decommissioning or transforming legacy applications, data migration, security, privacy, etc.
EAs will also be mentoring the team to move an organization toward its target architecture.
Myths
There are a few myths that organizations should be aware of before employing an enterprise architect and employing an EA strategy. Enterprise architect myths include:
- EA has no value for agile companies: Even though agile companies cover some aspects of EA's role, they still miss out on the benefits of data-informed business transformations, time efficiency, and risk management.
- EA is a one-time effort/used for one-off projects: EA requires a continuous effort to produce value for an organization, and should not be viewed as a one-off exercise.
- If you follow TOGAF, you must be a good EA: TOGAF is considered the best framework, but in practice, EAs most often use pieces of different frameworks at once to fit their organization and EA tool.







/EN-WP-EA-Tomorrow-Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EN-WP-EA-Tomorrow-Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)