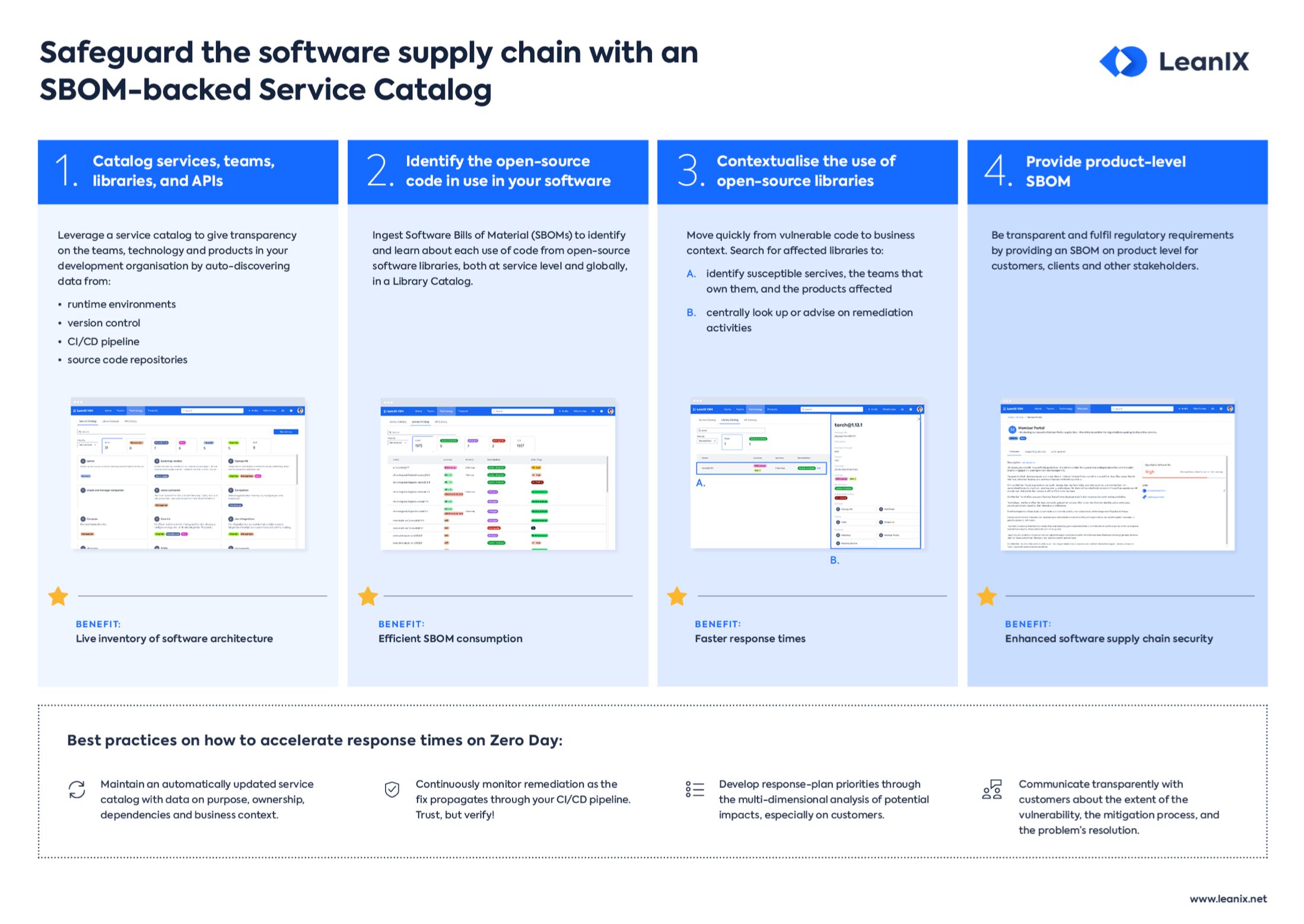
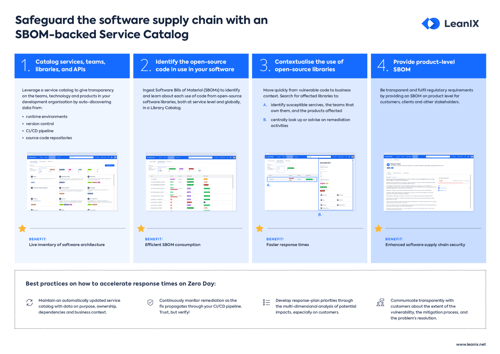
Introduction
In an interconnected digital world, software supply chains—processes that convert initial code into final software products—are complex and potentially fraught with security risks.
Threat actors often exploit vulnerable points in these chains, leading to serious consequences like data breaches or service disruption.
It's crucial for organizations to understand these risks and secure their software supply chains effectively.
But what is it, why is it important, and how does it relate to the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM)?
What is software supply chain security?
Software supply chain security is the practice of protecting and securing all elements involved in the software development process, including third-party services, open-source libraries, internal development tools, and deployment environments.
This concept goes beyond the scope of traditional application security. It ensures the integrity and confidentiality of your software products from inception to end-of-life.
But what exactly is a software supply chain?
A software supply chain encompasses all activities and entities involved in the creation, delivery, and maintenance of a software product. This includes the ideation and design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance stages of software development.
It also involves various entities such as software developers, third-party service providers, open-source libraries, internal development tools, and deployment environments.
Ensuring the security of this supply chain goes beyond the scope of traditional application security. It aims to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of your software products from inception to end-of-life by mitigating potential risks in all components of the supply chain.
Solarwind example
One of the most notable examples of a software supply chain attack is the SolarWinds incident.
In this case, malicious actors compromised the update mechanism of SolarWinds' Orion software, a network monitoring tool used by numerous organizations worldwide.
This compromise allowed the attackers to distribute malicious updates to Orion customers, leading to a significant breach affecting several high-profile organizations.
Software supply chain security v.s. application security
While software supply chain security and application security might seem similar, they cater to different aspects of software protection.
Application security focuses on the security of software applications from malicious attacks and threats, focusing primarily on the code and features of the software application.
On the other hand, software supply chain security involves ensuring the security of the entire development and distribution process.
It focuses not only on the software application but also on the various components and parties involved in its creation and maintenance. This includes open-source components, third-party vendors, and internal development practices.





/EN/Tools/EA-Maturity-Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EA-Maturity-Thumbnail.png)