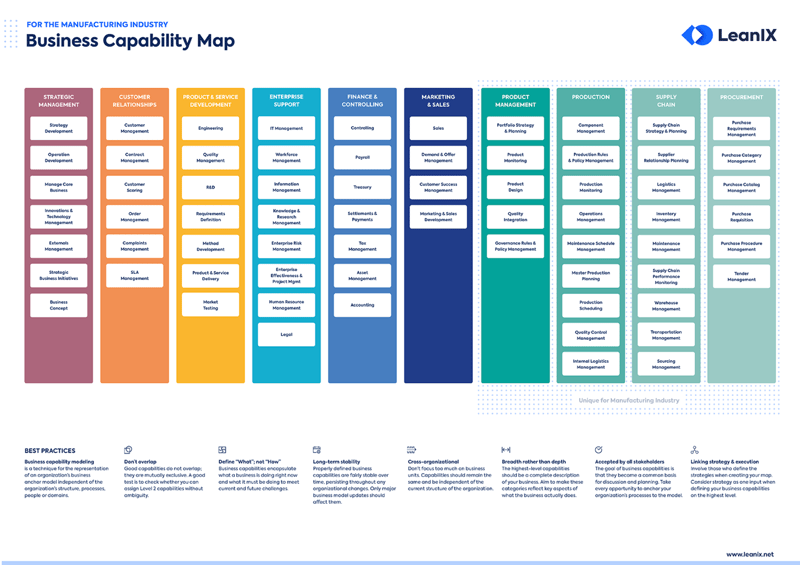
The nine pillars of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 manufacturing is based on state-of-the-art digital technologies. These technology trends form the nine main pillars of Industry 4.0:
1. Big Data analysis
Data sets influence the strategy and daily operations of an enterprise. In the age of Industry 4.0 manufacturing, data is collected and evaluated from various sources such as machines, production goods, and systems. All four classic Big Data approaches are used here:
- Detailed analysis (Descriptive Analytics)
- Precise diagnosis (Diagnostic Analytics)
- Looking to the future (Predictive Analytics)
- Instructions (Prescriptive Analytics)
On the basis of these analyses, you maintain an overview of current market trends and customer preferences, can minimize risks, and react quickly to changes.
2. Cloud computing
The cloud transmits and stores data and makes it available for further use. It offers an ideal solution, especially for large amounts of data that are shared across multiple locations and company boundaries. There are three different models for a cloud platform: Saas (Software-as-a-Service), IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), and PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service).
For example, the industry can benefit from intelligent home networking, better maintenance services, regular updates, and personal assistants. Reducing energy consumption compared to stationary storage not only saves your company money but also protects the environment. Especially with the increasing complexity of cloud landscapes, an Enterprise Architecture Framework is essential. Only in this way can the agility of digital innovation projects be maintained.
3. Autonomous robots
Robots have been around for some time. However, they have never been as advanced as they are today. They bring a decisive advantage in industrial use when solving tasks that are beyond the capabilities of humans.
4. Simulations
Simulations make it possible to get to know potential operational activities before implementation. Where can something go wrong? How can I prepare for the challenges? By mapping the physical world in a virtual model, machine settings can be tested and optimized in advance. This allows you to react to potential issues in advance, reduce production times, and increase quality.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things is one of the main pillars of Industry 4.0 Manufacturing. It enables communication between individual components. Every device or product collects data and sends them to the Internet, where it can be processed and distributed. IoT is strongly dependent on a hierarchy. While devices at the lowest level collect data, highly complex devices make decisions based on this data. The decentralization of analysis and decision-making enables real-time responsiveness.
6. Horizontal and vertical system integration
Horizontal integration considers the entire supply chain. It allows machines, IoT devices, and other components to work together seamlessly across company boundaries. For example, manufacturers, suppliers, and customers merge into a digitally networked, value-added unit.
Vertical integration considers the entire value chain. It optimizes processes within individual hierarchical levels - for example, production management level, corporate planning level, or execution level. The various systems of production are integrated to form a consistent solution.
7. Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is probably better known as 3D printing. With these manufacturing processes, it is possible to develop customer-specific products in a cost-efficient and environmentally friendly way.
8. Augmented reality
Augmented reality is used in Industry 4.0 manufacturing to create a connection between man and machine. Humans can look at something and get a computer-generated idea of how it will look and perform. For example, designers can see and experience a product before project completion.
9. Cybersecurity
With Industry 4.0 manufacturing, the use of technologies and networking of different components is continuously on the rise. Protecting the production process from possible cyberattacks is critical to avoid disruptions. Cybersecurity protects data and also detects harmful patterns to prevent unauthorized interventions before they happen.

5 steps to success in Industry 4.0
In general, for the right concept of introducing Industry 4.0 manufacturing, each company must be considered differently. Various factors like factory requirements, product types and variants, or production processes play an important role in the path to Industry 4.0. However, there are five general steps that have been identified for a successful implementation.
1. Networking
Intelligent networking is the first step on the road to success in Industry 4.0: Machines, products (parts), and other components are connected to a common network. Through machine-to-machine communication, data can be used for automated production and autonomous decisions can be made.
2. Collect
Once the networking has been successfully implemented, production data is collected and stored. For safety, production and quality data can be viewed and tracked at any time. Special attention should be paid to the security of data storage and data transport. Especially when handling sensitive and confidential information.
3. Visualize
The visualization of the data on predefined dashboards supports the discovery of insights. The data can be broken down to the smallest detail to provide an overview of, for example:
- the most frequent errors per machine and shift,
- the overall quality of production, or
- the most common machine errors that reduce quality.
For the right conclusions and to improve production, the interpretation of the data must be done by an expert with deep process knowledge.
4. Analyze
Here, the aim is to imitate the knowledge that experts gain from data. The plant data must be linked to process knowledge. This makes knowledge available around the clock - improving productivity, quality, and uptime. Optimization tasks can be implemented by regular experts.
5. Automation
In this step, the actual mission of Industry 4.0 is fulfilled. The machines organize and decide independently during the entire production process. Plant operators only approve parameter changes that are carried out by the machines themselves. Maintenance personnel is coordinated by the machines that need service.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 is the future standard for staying competitive in the market and fully exploiting innovation potential. The be-all and end-all for a successful entry into Industry 4.0 is a precise overview of the company and the development of a future-oriented strategy.
The IT sector, in particular, plays a key role here, as the growing number of applications and increasing networking requirements are more demanding than ever. This makes it all the more important to rationalize IT applications to the bare essentials and standardize uniform applications across the enterprise.
This is exactly where LeanIX comes in. At the NORMA Group we have successfully implemented the roadmap for the rationalization of applications.

/EA-Manufacturing-WhitePaper_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=400&height=283&name=EA-Manufacturing-WhitePaper_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)
/EA-Manufacturing-WhitePaper_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EA-Manufacturing-WhitePaper_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)
/EA_24Views_Manuf_Industry_Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EA_24Views_Manuf_Industry_Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)