Introduction
The formalized practice of data modeling has occurred since the 1960s and has grown steadily in importance ever since. Today it is commonly utilized by IT professionals to identify the requirements necessary for handling data for the purposes of better supporting the business objects of an organization.
Just like how when moving into a new house, individuals tend to map out where to place furniture, electronics, etc., data modeling minimizes the difficulty of adapting to new environments and simplifies decision-making in complex situations.
As such, data modeling has become an integral part of maintaining the IT landscape and ensuring an efficient means of storing and analyzing data.
What is enterprise data modeling?
Data modeling is a process for conceptualizing the relationships between different types of information in an organization, independent of the organization’s structure, processes, people, or domains.
Data models are a representation of data objects and the relationships between those objects which helps users across disciplines store and interact with data more effectively for a variety of use cases.
This visual guide helps when performing data governance and creating data policies. Data modeling is a way to help organizations become more data-driven.
Source: LeanIX GmbH
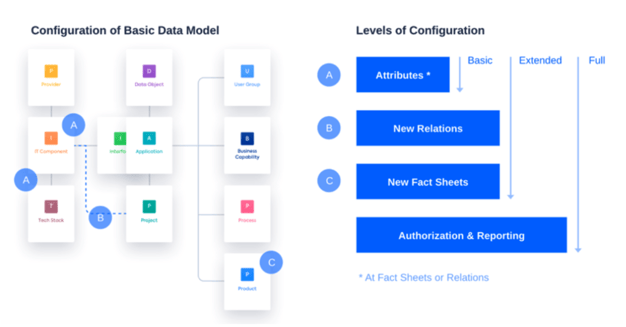
IT professionals design data model structures based on the actual ways in which IT entities, personnel, and business capabilities interface with one another. Such objects become the main categories, or boxes, in the model. These objects are all interconnected, and the connections (or relationships) between the items are used to visualize data and guide policies governing this data.
When creating a data model to represent the infrastructure of an information system, it is important to make the models logical and easily understandable for those requiring insights on data objects in relation to their business needs.
Overall, the process of data modeling entails defining the attributes of all data objects and connecting the relationships between the different types of information that need to be stored. This map, or diagram, helps IT professionals understand what key data needs to be stored and easily retrieved.
Why should you use data modeling?
Data models reflect data that are absolutely essential for a business's continuing operation. Its structure helps align databases across the physical, conceptual, and logical levels. The primary goals of using data modeling are:
- Users can take advantage of having this information neatly structured to identify technical and functional overlap, foster business intelligence, and optimize how data are organized.
- Controlling how and where data interact in either a server or cloud environment is crucial for implementing systems that equally benefit business and IT professionals.
- A data model can be used to validate the technical and functional benefits of current and future data objects while also revealing if databases are correctly represented.
Thanks to easy-to-understand representations of the underlying data, it is particularly helpful for developers when creating a physical database (e.g., missing or redundant data can be easily spotted to save time for developers).
If data is not accurately represented, there is a greater likelihood of false outputs from analytics reports and miscalculated strategic decisions.
Though it is easy to become overwhelmed by manual documentation efforts when outlining a data model, the efforts are invaluable when upgrading infrastructure.
Benefits of data modeling
There are benefits to using data models of all types.
- The first of which is being able to reliably ensure that data objects in an IT landscape are correctly represented.
- This information can then be utilized to define connections between primary and foreign keys, tables, and procedures.
- A data model can then be used to build a physical database if sufficiently detailed.
- Data models can also be leveraged to communicate to business stakeholders throughout organizations.
- Locating accurate sources of data to auto-fill the model.
Challenges of data modeling
Unfortunately, there are also some challenges when using data models. In order to effectively create a data model:
- The creator should have a firm understanding of the characteristics of the data that is already physically stored.
- A data model is also a system that can result in complex application development, thereby making these processes difficult to manage as well.
- All changes to the data model, both large and small, require developers to modify the entire application system.
/EN/Poster/EN-Data-Objects-Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=360&height=256&name=EN-Data-Objects-Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)


/the-complete-overview-of-enterprise-integration-patterns.png?width=260&height=171&name=the-complete-overview-of-enterprise-integration-patterns.png)