
Data protection has been a top issue from the European Union since the draft of the Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal data on January 28th, 1981. This convention was the first legally binding international instrument in the data protection field, and the European Union has continually enacted laws and regulations ever since.
Keeping with the trend of data protection, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was adopted on April 27th, 2016 and will be fully enforced on May 25th, 2018.
What is the purpose of GDPR?
At its most basic level, the GDPR requires organizations to fully understand what information they have collected, who has access to the information, and where the information is stored. Going forward, businesses must protect privacy-related user information.
How GDPR Will Affect US-Based Companies
Contrary to what the name suggests, the GDPR does not only affect European businesses but any firm that collects the data of European citizens including European e-commerce clients and companies with satellite offices staffed with European employees.
GDPR focuses on Personally Identifiable Information (PII) which is defined as any information that can be used on its own or with other information to identify, contact, or locate a single person, or to identify an individual in context. PII can be sensitive or nonsensitive. PII includes biometric information (e.g. gender, birth date, etc), medical information, personally identifiable financial information, and other sensitive identifiers such as driver's license information, passport or Social Security numbers. This information is routinely collected throughout normal e-commerce transactions, customer correspondence, and website analytics.
What Changes Will GDPR Bring to US Businesses?
Organizational changes, stricter application management, and increased transparency for the storing and management of data. Just understanding where data is stored, how to quickly access it, and modify data based on the needs and concerns of the customer is a simple directive that can be tricky to streamline for a US business that operates globally.
Major changes include:
- DATA PROTECTION THROUGH TECHNOLOGY (ART. 25 GDPR)
Companies are required to define internal strategies and initiate steps to ensure data protection through technology (by design) and as a standard approach (by default). Possible measures include minimizing and pseudonymizing the processing of personal data. - ACCOUNTABILITY (ART. 5 GDPR)
Companies are required to ensure and demonstrate adherence to data protection regulations, for example through certification. - NOTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS (ART. 33 GDPR)
Companies are required to report data breaches (e.g. through hacking attacks) immediately, within 72 hours, to the competent supervisory authority and the affected data subjects. Failure to do so may lead to fines of up to 20 million euros or 4% of the company's global annual turnover. - ENHANCED RIGHTS FOR INDIVIDUALS (ART. 17 GDPR)
These include the right to be forgotten, the right to request the porting of one’s personal data to a new organization, the right to object to certain processing activities, and the right for certain data to be deleted.
5 steps to comply with GDPR
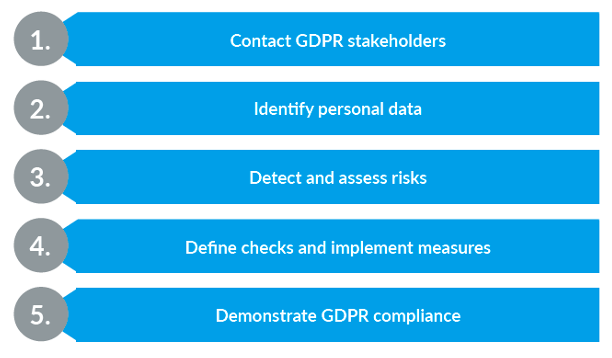
Read our in-depth article to GDPR compliance here.
Penalties for noncompliance with GDPR will be very costly but are avoidable if your firm is prepared before the enforce date.



