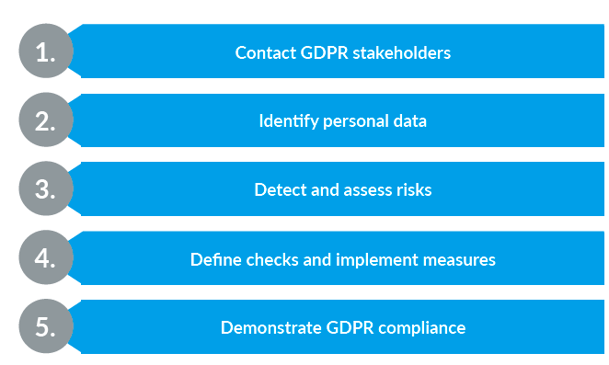
In our third and final blog in the series, "Mastering the GDPR with Enterprise Architecture," we highlight the 5 steps to GDPR compliance.
1. CONTACT GDPR STAKEHOLDERS
Contact other GDPR stakeholders to coordinate your next steps: in many organizations, EAs do not have final responsibility for compliance with legal regulations. This responsibility may lie with your legal department, the chief risk officer, the chief compliance officer, the chief information security officer or the data protection officer. Contact these people in order to coordinate your actions.
In our third and final blog on the series, "Mastering the GDPR with Enterprise Architecture," we highlight the 5 steps to GDPR compliance.
2. Identify personal data
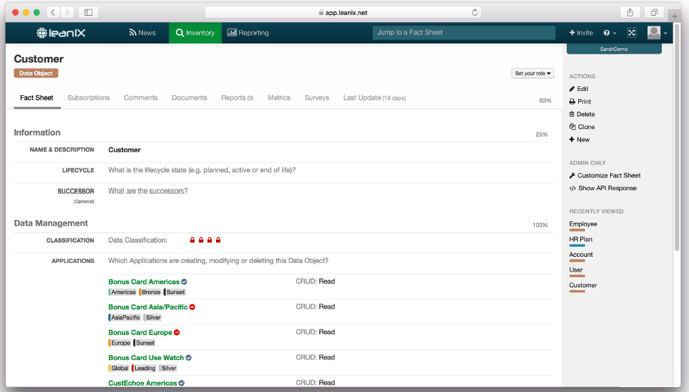
Creating a data inventory is crucial to meeting the requirements of the GDPR documentation. The key to smooth implementation is your data; you will, therefore, need to gain a clear overview of the data processing in your company. Collecting this information is no easy task, it may take a lot of time and you presumably do not have all the information you need. Consider using an EAM software for this organization.
LeanIX features like Survey and Heap Maps can help you localize any applications that process sensitive data and identify business capabilities that use the applications in question. The features will also resolve many pertinent unanswered questions, such as: "Who is responsible for the processing of personal data? Which applications use these data? Are they additionally processed and stored outside the EU?"
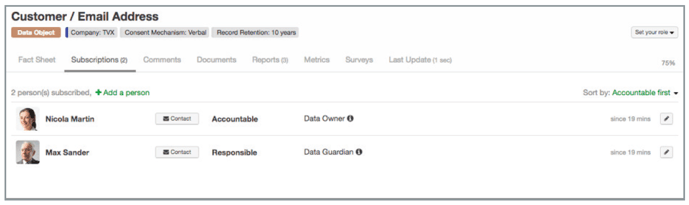
Figure 3 -Identifying responsibilities and ownership of data objects in LeanIX
3. Detect and assess risks
Around 76 percent of German businesses state that the complexity of modern IT services means they do not always know where exactly their customer data are located. Imagine a consumer wants to make use of her "right to be forgotten". In order to delete her data, you have to know where they are stored. LeanIX also has options to help your organization effectively implementing these processes.
Data Flow Model, which is an automated visualization, shows which data objects are used by which applications and which business capabilities, in turn, depend on them.
The data flow is generated automatically and can be expanded by adding details such as the IT components and user groups of certain applications. Labels next to the interfaces display their attributes, such as interface technology, data objects, and frequency. Then assess your application landscape for risk. The level of risk can be determined through a range of different parameters, in particular with regard to the business impact, application dependencies, criticality levels, failure scenarios and previous incidents.
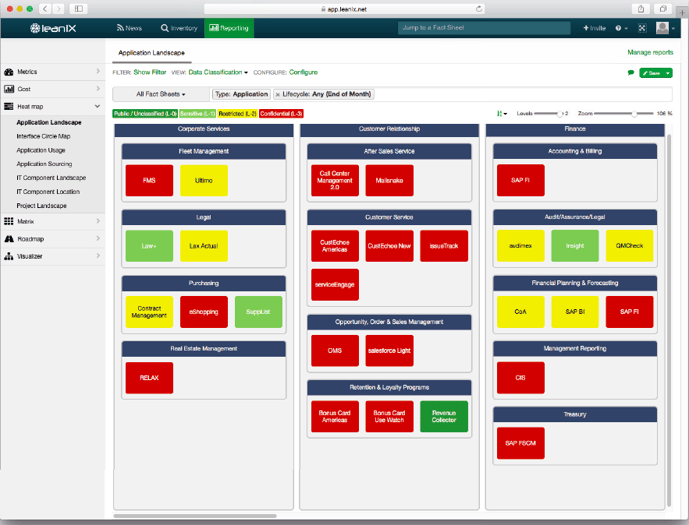
Figure 4: Classifying data with Heat Maps in LeanIX
Visualizations such as the above-described Heat Map (fig. 4) can provide information on business-critical consequences for your company in the event of an application failure or hacking attack. Risk Dependency Maps and Interface Circle Maps visualize the various dependencies between multiple applications. The more dependencies an application has, the higher the level of risk in the event of a failure. You can additionally use a Survey when querying information on possible failure scenarios and incidents in the past in order to assess the risk level.
4. Define checks and implement measures
Once you have correctly assessed the technology risks, you need to implement concrete security checks and preventative measures. The IT security checks in ISO 27001 can serve as a guideline here. Introduce important measures as soon as possible in order to implement the data protection by technology approach (e.g. pseudonymization personal data); this will save you time and money when upgrading. Always ask yourself: How well does your application portfolio meet security standards? And how are your security standards developing over time? The aforementioned LeanIX Survey feature will help your enterprise answer these questions.
5. Demonstrate GDPR compliance
Demonstrate your compliance with GDPR guidelines by showing how you process personal data, how you handle risks and what measures for damage limitation you have implemented. The latter is especially relevant when you conduct a DPIA, which the GDPR requires for every implementation of a new system that uses personal data. Use e.g. the LeanIX Inventory View function and present your GDPR compliance by providing a quick and clear overview in table form of all applications, interfaces, data objects, and technologies.



