Enhancements
SAP Enhancements are added if the business requirement cannot be satisfied using standard SAP features. During large implementations, an SAP standard blueprint will be prepared and followed. When business requirements cannot be achieved using a standard blueprint, project teams will add some custom functionalities by modifying the solution – these are called enhancements.
Enhancements are created by ABAP teams who make use of BADIs, enhancement frameworks, or user exits. These will then become the RICEFW objects the project teams work with to modify or leverage the SAP standard. Another option is to create new custom solutions based on business requirements and target architecture.
An example of an SAP enhancement is to develop Radio Frequency Mobile Data Entry (RF) capabilities at the Inventory Management (IM) level. Standard SAP has given the RF at the WM or EWM level. When a client manages a warehouse on the IM level and is looking for RF capabilities, the enhancement is needed to meet business objectives.
Forms
SAP forms are simply print outputs created by the SAP application after saving transactional data. These forms can be the development of layouts for invoices, account statements, delivery notes, purchase order print, etc. SAP Standard provides a template for all these forms.
If they do not meet specific business requirements (i.e. company logo or print legal text), the functional team will need to work with ABAP to develop custom forms for each specific need.
Workflow
The last RICEFW object is SAP workflow. Workflow refers to the sequential flow of transactional data from one level to another as per the organization’s hierarchy. At each level, actions are required, and once taken, the workflow will advance to the next level.
During this objective, the functional consultant coordinates with the technical team to develop custom flow logic. These will contain the details of the data to be sent and will provide the conditions to trigger the workflow.
For example, budget approvals handling. A purchase order is created for a value and sent to the manager for approval. When approved, it will go to the VP for further approval, and so on until signed off. In this case, the business requirement is not available in a standard SAP application, so the result is a new RICEFW object.
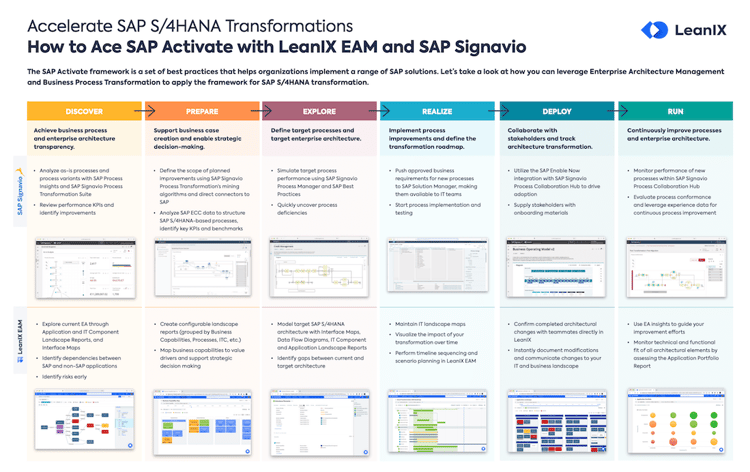
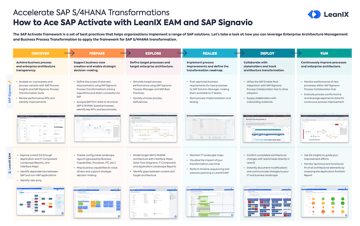
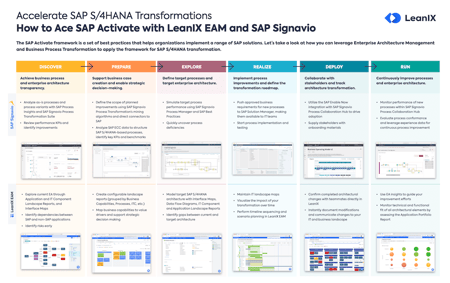
How is RICEFW used in a S/4HANA project?
Both, the Explore and Realize phases of the SAP Activate methodology require RICEFW objects to achieve the specific business processes and goals. This is especially important during S/4HANA transformation so that all customer-specific requirements are integrated into the solution. This way, business users are able to perform their daily tasks using their SAP system.
The S/4HANA RICEFW objects are identified mainly during Fit to Gap analysis sessions which take place during the Explore phase. This is where project teams identify which non-SAP solutions need to be integrated.
During the Realize phase and testing activity, a cutover plan is created. This moves the S/4HANA WRICEF objects into the production system which will eventually be used by the business in real-time.
Conclusion
The creation of SAP RICEFW objects is a process during the Explore phase of the SAP Activate methodology to identify third-party systems integrated within SAP.
The result of the RICEFW template is a customer-specific solution that meets the unique business requirements identified earlier in the transformation process.
It is essential that SAP project leads and architects identify all the requirements so the business systems and processes will run smoothly once migrated. Establishing and reporting to SAP CoE proves to be very helpful.

/EN-S4Hana-Roadmap-Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=400&height=280&name=EN-S4Hana-Roadmap-Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)
/EN/Reports/EN-LX-SAPS4HANA-Survey-Resource-Page-Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EN-LX-SAPS4HANA-Survey-Resource-Page-Thumbnail.png)
/EN/White-Paper/EN-SAP-Getting-it-Right-WP-Page-Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EN-SAP-Getting-it-Right-WP-Page-Thumbnail.png)
/EN/Video/Webinar-Thumbnail-360x250@2x-2.png?width=260&height=171&name=Webinar-Thumbnail-360x250@2x-2.png)
/EN-WP-SAP-S4Hana-Migration-Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EN-WP-SAP-S4Hana-Migration-Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)