What is the application criticality matrix?
An application criticality matrix is a way for IT architects and application owners to list and prioritize the applications in their portfolios.
The applications are ranked based on how critical they are to the organization. Thus, it’s easy to determine which are the most important.
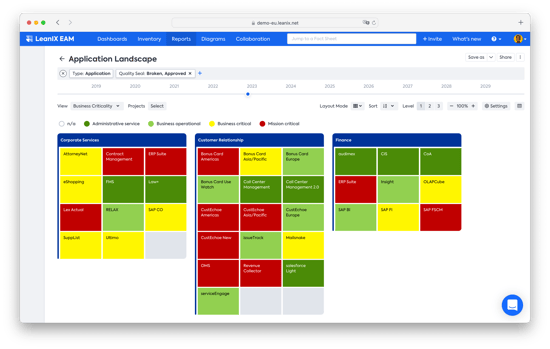
Application landscape report with business criticality view available in LeanIX EAM.
The application criticality matrix is also known as asset criticality, system criticality, or business criticality matrix.
A new matrix can be created for various different assets. Hence, the names of each level will usually be specified for each industry or business.
But even if the names of the levels are different, the context stays the same.
Why is the application criticality matrix important?
The application criticality matrix is important because it allows everyone in your team to understand each level of the matrix.
From this starting point, processes can be defined that improve, enhance and protect the organization’s most vital assets from risk.
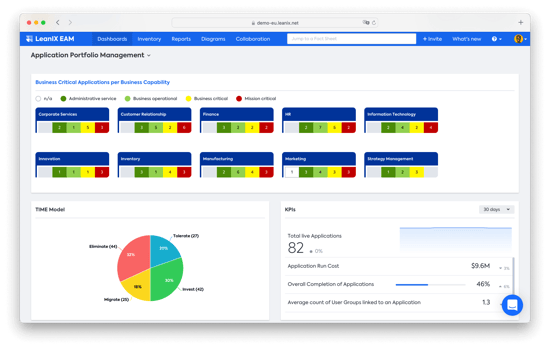
Classification - categories of matrix
The application criticality matrix is made up of four quadrants—mission-critical applications, business-critical applications, business operational applications, and administrative applications.

Business Criticality Levels available in LeanIX EAM surveys.
Other industries or businesses can also use the matrix with two axes only. The x-axis represents the likelihood or probability of an application's failure, and the y-axis represents the impact or consequence of the failure on the organization.
Since the classifications in both options are very similar, we will only explain one - the four quadrants.
1. Mission-critical applications
In an application portfolio assessment, mission-critical applications (MCAs) are software applications that perform an essential function in business operations. Mission-critical systems can consist of any kind of IT component including software, hardware, processes, applications, etc.
Organizations rely on mission-critical applications to run their business activities successfully, and any failure or disruption can be catastrophic. These applications must be available to run at any cost.
2. Business-critical applications
A business-critical application is a label given to business-critical processes, software, and services that require consistent availability. While breaks in service are not catastrophic, they are highly undesirable. Business-critical applications should be consistent and reliable.
Factors that determine business-critical applications are whether they can cause reputation damage, sensitive information loss, financial loss, or some kind of operational risk.
3. Business operational applications
Business operational applications are the next label in our application criticality matrix. These are also fairly non-critical applications that contribute to running efficient business operations.
When they are disrupted it can cause problems within the organization. However, they are out of the direct line of service to the customer.
Business operational applications provide business functionality such as communication tools, CRM applications, finance services, and other applications that help the organization function.
4. Administrative applications
Lastly, administrative service applications tend to be those that are low-priority and non-critical to everyday business operations. When these applications fail it can cause some problems but it will not affect the customer and can be tolerated a bit more.
Factors include applications for record keeping, mail services, and office upkeep.




/EN-12StepsBetterIT_Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EN-12StepsBetterIT_Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)
/WhitePaper_Resource_Page_Def_Guide_to_APM.png?width=260&height=171&name=WhitePaper_Resource_Page_Def_Guide_to_APM.png)
/LeanIX_Poster_Best-practices-to-define-energy-business-capability-maps.png?width=260&height=171&name=LeanIX_Poster_Best-practices-to-define-energy-business-capability-maps.png)