In their efforts to deploy and apply Artificial Intelligence (AI) in their organizations, many companies are facing certain challenges, lack of resources and skills being among the most significant ones. This blog series will explain what AI is and explores how it can create value for your business right now, as well as the necessary steps to take before any AI-based solution can be deployed. We will look at several use cases and success stories from different industries that show how AI is applied successfully today.
AI is expected to thrive in the enterprise, bringing transformative changes in how enterprise software is designed and uses data to produce better results for customers. Enterprise Architects should start thinking now about how your organization can benefit from using it. AI will offer capabilities like predictive analytics, thereby reshaping your decision-making process and ultimately improving the way you and your enterprise work.
The state of AI
Gartner defines AI as technology that appears to copy human performance typically by learning, drawing its own conclusions, appearing to understand complex content, engaging in natural dialogs with people, enhancing human cognitive performance, or replacing people during the execution of non-routine tasks.
Based on this definition, AI is a very broad term that includes Machine Learning (ML). These terms are often used interchangeably, which creates a lot of confusion. Simply put, AI is the broader concept of machines that can perform tasks in a “smart” way, whereas ML is a current application of AI-based on the idea that we should be able to give machines access to data and let them learn for themselves.
When looking at the agenda of the prominent analyst and consulting firms, it seems ML took the place of big data as the “shiny new thing” in technology, and will be one of the biggest disruptors for big data analytics in 2017.
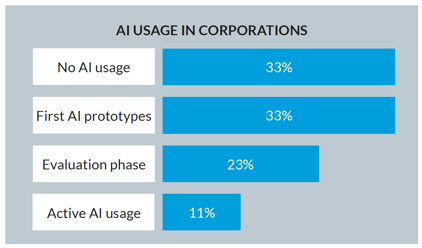
Despite the significant interest generated around ML, there is a large gap between research and beneficial use cases of AI in the real world. Only a small number of companies have the resources to actually drive AI innovation and deliver it to the masses. A New Forrester Research survey, which polled 612 business and tech professionals to gauge the enterprise AI research scope, shows that 58 percent of the respondents said their organizations are researching AI, while only 12 percent use AI systems at work.
Experts see AI as an essential support tool for humans using technology in every aspect of life, especially in commercial applications. A LeanIX survey about the state of AI 2017 comes to similar results.
What makes AI valuable in business is its capability to process and analyze massive amounts of data faster than a human brain could. Based on the courses of action that AI suggests, humans can eliminate possible consequences of each action and streamline the decision-making process.
AI is equally valued for its versatility in business areas ranging from cybersecurity, because of scale and growing complexity, to customer relationship management (CRM) by turning the CRM system into a self-updating system that stays on top of companies’ relationship management, to finance by integrating AI into regular banking operations, such as mortgage loans.
In the future, intelligent apps will transform every existing software category with AI-enabled capabilities, from security tooling to enterprise applications such as marketing or ERP. Using AI, tech providers will focus on three areas — advanced analytics, AI-powered, and increasingly autonomous business processes, AI-powered immersive, conversational, and continuous interfaces.
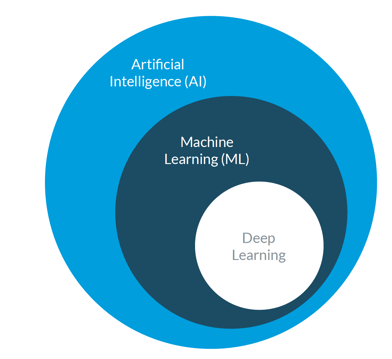
Figure 1: How Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning relate
How to understand AI
The specific pain points regarding AI use in enterprises are both the big gap between research and actual beneficial usage, and the lack of resources to drive and deliver AI innovation to the masses. Despite the growing interest in AI, only 12% of the business and tech professionals surveyed by Forrester Research use AI at work, while 58% of them are researching it. The LeanIX State of AI Survey 2017 confirms that only around 11% of companies constructively apply AI.
To benefit from the transformative value of AI today, it is important to understand that AI is composed of technology building blocks that, individually or combined, are advanced enough to add a degree of intelligence to applications that can lead to considerable business transformation.
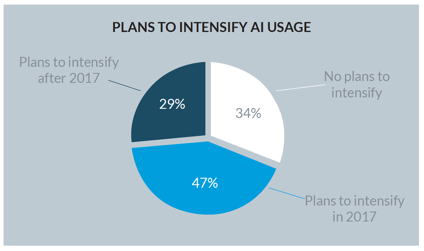
How AI improves business processes
In a world in which business decision-makers are under pressure and must act fast, there’s little time left to review, research, and analyze every piece of information and understand all its implications. Systemized processes and ERP systems are crucial for basic business workflows.
However, AI can improve compliance effectiveness and reduce costs without sacrificing operational efficiency by automating the activities of human review, research, and decision-making. In other words, AI empowers rather than replaces decision-makers. Even though we may be far from a time when computers can reproduce the human intelligence needed for more refined business analysis and recommendations, almost all high-value work performed by humans is amplified by more complex tools. The increasingly intelligent suggestions made by technology are the foundation for the informed decisions humans make based on their own experience and intuition.
In the modern era, there have been many advocates of a business process-centric enterprise architecture. Regardless of the structures, business processes are designed by humans with relevant expertise and reflect their vision, knowledge, and the organization’s mission.
Technological progress, rapid information growth, and the coming out of instant communication have broad implications on how an enterprise architect itself. To be successful, enterprises need to rethink every aspect of their business from the ground up. In the future, experts estimate that machines will assume a growing execution role and will assist humans in the design aspect with assembled intelligence that humans cannot collect on their own. However, humans will instruct the machines to assemble this intelligence and will continually monitor and fine-tune the process



